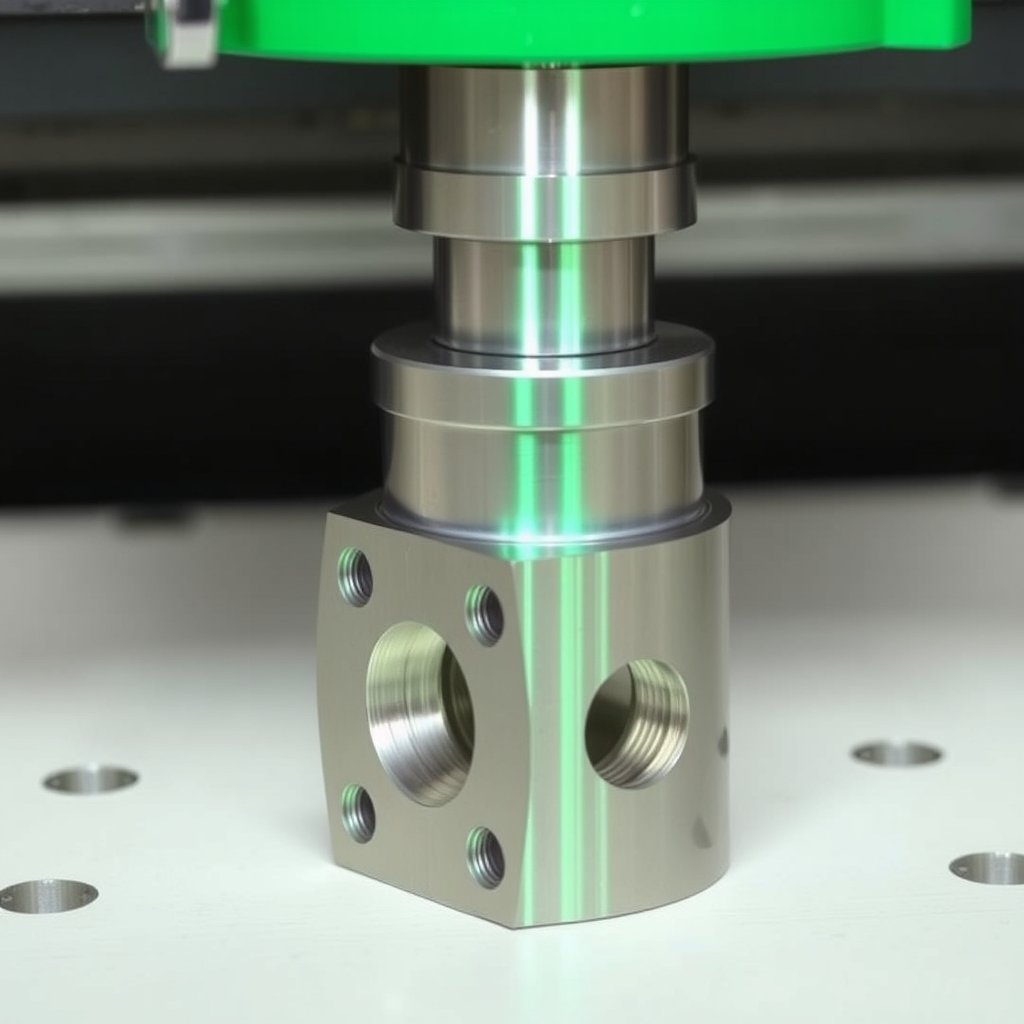
Introduction to CNC Machining
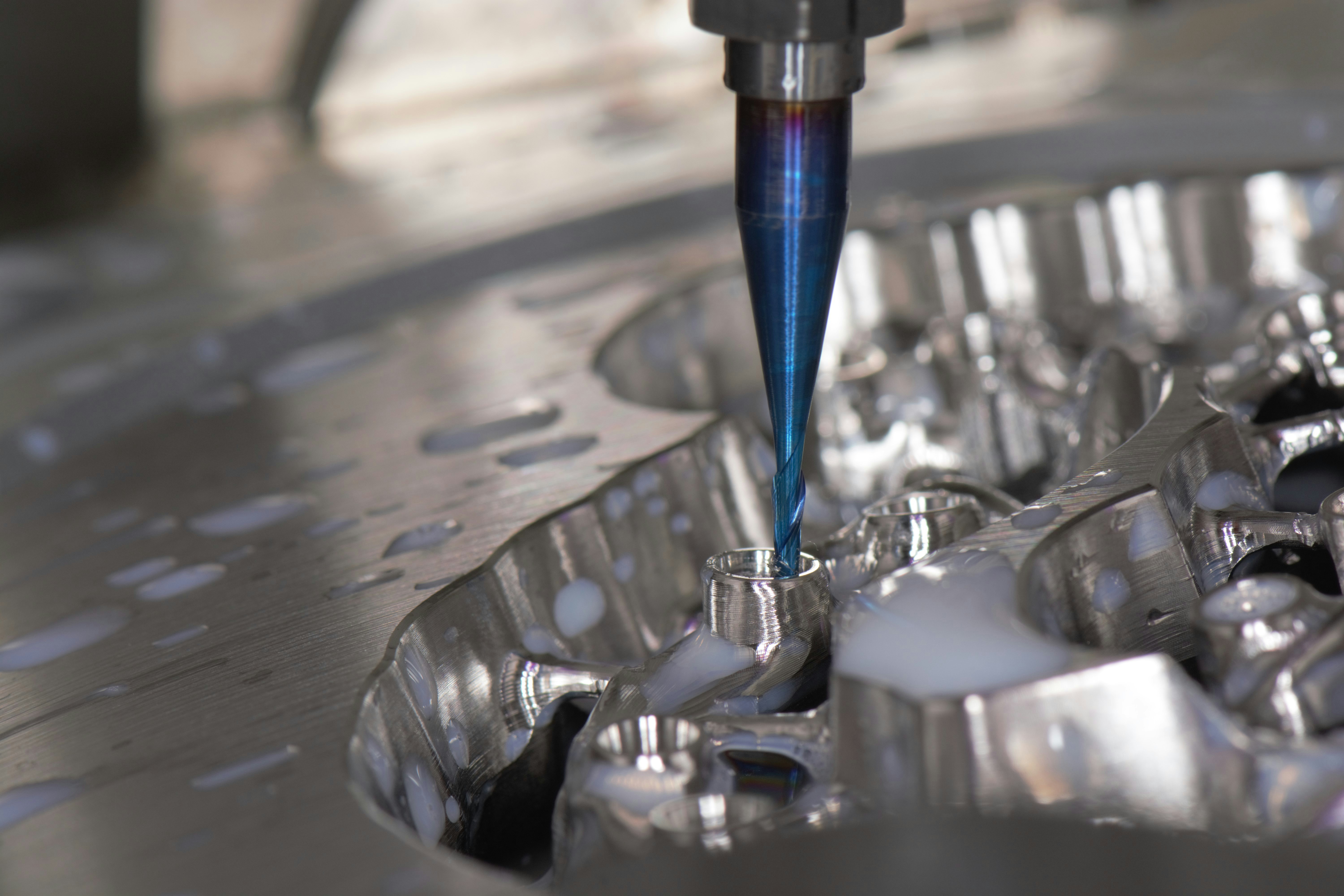
CNC machining, or Computer Numerical Control machining, represents a significant advancement in the manufacturing and engineering sectors. The technology facilitates the automatic control of machine tools through the use of computers, which enhances the precision and efficiency of fabricating parts compared to traditional machining methods. Traditionally, manufacturing relied heavily on manual techniques, which often resulted in variability and inconsistencies in the finished products. CNC machining has revolutionized this approach by introducing automation, ensuring that machining operations are executed with remarkable precision and repeatability.
The transition from manual to CNC technology marks a pivotal shift in manufacturing paradigms. With CNC machines, complex shapes and intricate components can be produced consistently, which is particularly beneficial in high-volume production settings. The digitalization of the manufacturing process allows engineers and machinists to input specifications directly into the computer, which then controls the machinery to perform operations such as milling, turning, drilling, and grinding with minimal human intervention. This level of automation not only accelerates production times but also reduces the likelihood of human error, further enhancing the quality of the machined parts.
Additionally, CNC machining offers significant flexibility in design adaptations. Engineers can make quick adjustments in the software, leading to efficient revisions when needed without the downtime typically associated with traditional setups. This flexibility is indispensable in industries where customization and quick turnaround times are essential. Moreover, CNC technology is applicable across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer products, where precision and reliability are paramount. Overall, the significance of CNC machining continues to grow, underscoring its essential role in modern manufacturing and engineering processes.
The CNC Machining Process
CNC machining involves a series of methodical steps designed to transform a digital design into a physical part. The first stage in the CNC machining process is the creation of part designs using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. Designers utilize CAD tools to create detailed 2D or 3D models that accurately represent the dimensions and contours of the intended part. This digital representation serves as the foundation upon which the machining instructions will be based.
Once the design is complete, it must be translated into a format that the CNC machine can understand. This is achieved through a process known as CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), which converts the CAD files into G-code, a language that CNC machines use to execute the machining operations. The G-code contains specific instructions regarding how the machine should move, which tools to use, and how fast to operate, essentially bridging the gap between digital design and physical manufacturing.
The next critical step in the process is setup. This involves securing the raw material on the CNC machine and installing the appropriate cutting tools. Selecting the correct tooling is paramount, as it influences both the efficiency of the machining operation and the quality of the finished part. Factors such as material type, part geometry, and required tolerances play a significant role in tooling selection.
After setup, the CNC machine is programmed with the G-code generated earlier. This programming phase is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and repeatability of the machining process. Once these preparations are finalized, the actual machining can begin. The CNC machine automatically carries out the cutting, drilling, or milling processes according to the programmed instructions, efficiently producing highly precise components.
Through these systematic steps—design, programming, setup, tooling selection, and machining—the CNC process allows for the mass production of intricate parts with a high degree of accuracy and quality control.
Types of CNC Machines
CNC machines are integral to modern manufacturing, as they enhance precision and automation in part production. Several types of CNC machines cater to varying industry needs, each designed for specific applications and materials.
One of the most common types is the CNC mill. This machine utilizes rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece in a variety of shapes and sizes. CNC mills can create intricate parts with tight tolerances and are widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. The versatility of CNC mills allows them to handle materials such as metals, plastics, and composites. For instance, aerospace components often require the use of lightweight yet durable materials that CNC mills can efficiently process.
Another essential machine is the CNC lathe. Lathes are designed to shape materials by rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool. This type of machine excels in producing cylindrical parts, such as shafts, pulleys, and bushings. CNC lathes provide high accuracy and are ideal for manufacturers needing high-volume production of parts with consistent quality. They can work with a range of materials, including metals and plastics, making them a popular choice in various sectors.
CNC routers are also widely used in the woodworking and plastics industries. These machines operate similarly to CNC mills but are typically larger and designed for cutting softer materials. A CNC router can create detailed engravings and cut intricate shapes, making it ideal for furniture production, signage, and art installations.
Lastly, CNC laser cutters utilize focused laser beams to cut or engrave materials with high precision. They are perfect for thin sheets of various materials, including metals, glass, and plastics. CNC laser cutters are often employed in industries requiring detailed design work, such as jewelry making and signage fabrication. Each of these CNC machines plays a vital role in optimizing production processes across numerous industries, showcasing their unique capabilities that cater to specific manufacturing needs.
Materials Used in CNC Machining
CNC machining is a versatile manufacturing process that can accommodate a broad range of materials, each with unique properties that influence the performance and characteristics of the final product. The materials typically used in CNC machining can be categorized into metals, plastics, woods, and composites.
Metals are among the most common materials employed in CNC machining. Aluminum, for instance, is praised for its lightweight nature, excellent corrosion resistance, and favorable machinability, making it a preferred choice for various applications ranging from aerospace to automotive. Steel, on the other hand, offers strength and durability, albeit at the cost of increased weight. Materials like titanium, known for its superior strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility, are also machined but may require more intricate processing due to their hardness.
Plastics constitute another significant category in CNC machining. Common thermoplastics, such as polyethylene and polycarbonate, are lightweight and can be easily molded. They exhibit good resistance to chemicals and impact, making them suitable for a variety of applications, including consumer products and medical devices. However, plastics generally do not provide the same structural integrity as metals, which can limit their use in high-stress environments.
Wood, while less frequently machined than metals and plastics, offers unique aesthetic values. CNC machining can enhance precision in woodworking, allowing for intricate patterns and designs. The choice of wood species, such as hardwoods or softwoods, can affect the final product’s durability and appearance. Yet, wood can be susceptible to warping and moisture absorption.
Composite materials, which combine two or more constituents, have gained popularity in specialized applications. Their lightweight yet strong characteristics make them favorable in industries such as aerospace and automotive. However, the complexity in machining composites may lead to challenges, including increased tool wear and the potential for delamination.
Each material choice in CNC machining inherently carries its own advantages and disadvantages, impacting factors like cost, production speed, and the functionality of the final product. Understanding the characteristics of these materials and their implications on the machining process is crucial for engineers and manufacturers alike.
Advantages of CNC Machined Parts
CNC machining, which stands for Computer Numerical Control machining, offers several significant advantages that are transforming contemporary manufacturing processes. One of the primary benefits is the high precision achieved in the machining of parts. CNC machines operate with a high degree of accuracy, often to within a few microns. This precision is essential in industries such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where even minute discrepancies can lead to severe consequences. For instance, components for aircraft engines and orthopedic implants must meet strict tolerances that CNC machining can consistently deliver.
An additional advantage of CNC machined parts is their excellent repeatability. Once a CNC program is established, it can produce identical parts repeatedly without variance. This characteristic minimizes the risk of human error, which can occur in manual machining processes. For example, in a high-volume production setting, a single error can cascade into thousands of defective parts, leading to increased costs and delays in project timelines. CNC machining virtually eliminates this risk, ensuring that every piece, whether the first or the thousandth, meets the same specifications.
Efficiency is another notable benefit associated with CNC machining. The automation of the machining process results in faster production times, allowing manufacturers to meet urgent deadlines without sacrificing quality. This efficiency is particularly advantageous in industries that require rapid prototyping or quick-turn production runs. Furthermore, CNC machines can work continuously, reducing downtime and optimizing resource usage.
Finally, the flexibility in design offered by CNC machining is unparalleled. Designers can create complex geometries and intricate features without constraint, facilitating the development of innovative products. Consider the automotive industry, where custom parts are frequently required; CNC machining allows for swift adaptation to changing designs, which is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in a fast-paced market.
Applications of CNC Machined Parts
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining plays an integral role across a wide range of industries, providing precision and efficiency for the production of complex components. One of the most prominent sectors employing CNC machined parts is aerospace. In this industry, manufacturers require components that adhere to strict safety and performance standards. CNC machining enables the creation of intricate designs and geometries that are often required for aircraft components, such as brackets, housings, and turbine blades, ensuring high levels of accuracy and repeatability.
Another significant application of CNC machined parts is in the automotive industry. The demand for lightweight and high-performance components has driven automotive manufacturers to utilize CNC machining for producing parts such as engine blocks, transmission housings, and suspension components. The ability to produce complex shapes optimally contributes to improved fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Furthermore, CNC machining can facilitate rapid prototyping, allowing for the quick turnaround of new designs and updates, which is crucial in the fast-paced automotive market.
The medical device industry also heavily relies on CNC machined parts. Precision is vital in the manufacture of medical instruments, implants, and prosthetics. CNC machining offers the capability to achieve the tight tolerances required for these applications, ensuring that the final products meet regulatory standards for safety and efficacy. In addition, CNC technology allows for customization and personalization in medical devices, catering to specific patient needs.
Consumer goods manufacturers leverage CNC machining to develop a plethora of products that require high durability and aesthetic appeal. From electronics casings to furniture components, the versatility of CNC machined parts allows for mass production while maintaining quality control.
In conclusion, CNC machined parts significantly enhance the quality and performance across various industries, playing a pivotal role in the manufacturing process. As technology advances, the applications for CNC machining continue to grow, demonstrating its importance in modern manufacturing.
Quality Control in CNC Machining
Quality control is a fundamental aspect of CNC machining that ensures the produced parts meet the required specifications and standards. In a highly competitive manufacturing environment, the precision and reliability of CNC machined parts are paramount, as they directly impact the performance and longevity of the final products. Various quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to achieve the highest standards.
One of the primary inspection techniques utilized in CNC machining is dimensional inspection. This involves measuring the physical dimensions of machined parts to verify that they fall within specified tolerances. Utilizing tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) allows operators to detect deviations from the design specifications early in the production process. Such proactive measures significantly reduce the risk of defects and waste, enhancing overall production efficiency.
Tolerances play a crucial role in the quality control of CNC machined parts. Tolerancing defines the allowable variations in size and geometric features. CNC machining can achieve tight tolerances, often as low as ±0.01 mm, depending on the material and complexity of the part. It is essential for manufacturers to clearly communicate their tolerance requirements to CNC service providers to ensure that the finished product meets functionality and interoperability standards.
In addition to dimensional inspection and tolerances, adherence to industry standards also forms a critical component of quality assurance. Standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for establishing and maintaining quality management systems in CNC machining operations. By following these regulations, manufacturers can consistently deliver high-quality parts, fostering trust and satisfaction among customers. Ultimately, a robust quality control system is indispensable in CNC machining, assuring that finished products perform reliably in their respective applications, thereby sustaining a competitive edge in the market.
The Future of CNC Machining
The future of CNC machining technology is poised for significant transformation, driven by the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and innovative materials. These developments promise to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of CNC machined parts, ultimately revolutionizing manufacturing practices across various industries.
One prominent trend is the incorporation of AI into CNC machining processes. By utilizing machine learning algorithms, manufacturers can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize machining parameters and improve decision-making. This capability enables a higher degree of accuracy in the production of CNC machined parts, minimizing waste and reducing cycle times. As AI continues to evolve, its application in predictive maintenance will further bolster operational efficiency, allowing companies to anticipate issues before they impact productivity.
Moreover, the IoT is set to play a vital role in the future of CNC machining. The interconnectivity facilitated by IoT devices allows for real-time monitoring of machinery and production processes. This connectivity not only enhances responsiveness but also enables data-driven insights that can lead to continuous improvement. Manufacturers will be able to implement adaptive control systems that adjust machining operations dynamically based on real-time performance data.
Additionally, advancements in materials science contribute significantly to the evolution of CNC machining technology. The introduction of lightweight yet durable materials, such as carbon fiber composites and advanced alloys, allows for the production of high-performance components that were previously unattainable. These materials, combined with improved machining techniques, will enhance the speed and accuracy of the manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, the future of CNC machining is characterized by rapid technological advancements that will redefine manufacturing practices. The integration of AI, IoT, and advanced materials signals an era in which speed, precision, and efficiency are paramount, positioning CNC machining as a cornerstone of modern production systems.
Conclusion
In summarizing the discussion surrounding CNC machined parts, it becomes evident that these components play a pivotal role in contemporary manufacturing processes. The precision and efficiency that CNC machining offers are unmatched, enabling the production of intricate parts with tight tolerances and higher repeatability than traditional manufacturing methods. This technological advancement has revolutionized various industries, facilitating the creation of everything from aerospace components to intricate medical devices.
Furthermore, the adaptability of CNC machinery allows manufacturers to respond swiftly to the evolving demands of the market. Innovations in software, materials, and machine design continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with CNC machining. These advancements not only enhance the capabilities of CNC machined parts but also contribute to sustainability, reducing waste and energy consumption during production.
As businesses seek to optimize their operations and maintain a competitive edge, the significance of utilizing CNC machined parts becomes increasingly apparent. By integrating CNC machining into their project workflows, companies can achieve exceptional product quality and operational efficiency. Whether it is for prototyping or large-scale production, leveraging the benefits of CNC technology can lead to substantial advantages.
For those contemplating the use of CNC machining for their particular applications, now is an opportune moment to explore this dynamic field. Engaging with experienced CNC service providers can facilitate the realization of innovative designs while ensuring that the final products meet stringent quality standards. As the landscape of manufacturing continues to evolve, embracing CNC machined parts will undoubtedly remain a strategic decision for many organizations.
